Why you should use a unicode detection tool
Understandably, most people never think about different types of characters when they're sending transactional text messages.
However, there are a number of encoding standards that are used to send different characters. Each one uses a different number of characters to send the message. This is important, because it means that a message could be using more SMS credits than you thought, increasing the cost of your SMS traffic.
Let's quickly run through the 3 main character sets:
- GSM Character Set
- Extended GSM character set
- Unicode character set
The GSM Character Set
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications. It is the most commonly used character encoding standard for sending text messages. It includes all Latin alphabet characters, numbers, the most commonly used punctuation marks and some basic symbols.
Texts sent using GSM can be up to 160 characters long.
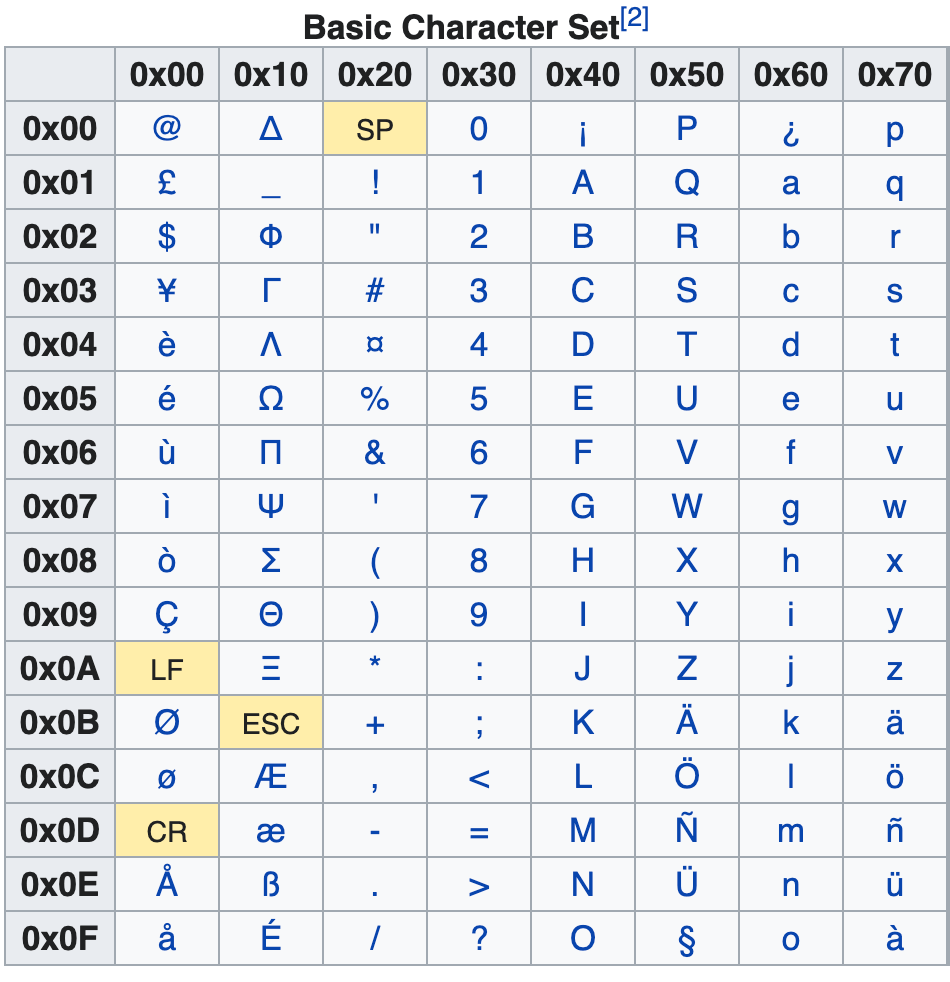
The Extended GSM Character Set
The extended GSM character set allows you to send 10 additional symbols that require 2 characters to be sent. The extended GSM characters are as follows:
£, ^, {, }, [, ~, ], €, LF (Line Feed), CR (Carriage Return)
The Unicode Character Set
The Unicode standard is a character encoding system that allows you to send a much larger range of characters than the standard Latin characters. It also allows you to send technical symbols and emojis.
Unicode encoding a text message reduces the number of available characters to just 70, rather than 160 that are permitted using GSM. Unicode characters require more space (2 bytes), rather than GSM characters that only use one byte.
Any unicode characters that are detected result in the entire message being sent as a unicode SMS, so the number of available characters reduces from 160 to just 70.
This can have a big impact on SMS credit usage, so it's vital to check that your messages are being sent using the encoding standard (GSM or unicode) that you intended.
What is the Unicode Character Detector?
The unicode character detector is a free tool that allows you to identify any characters in your text messages that are not part of the GSM character set.
Having identified any unicode characters, you can then make changes so that only GSM characters are used, increasing the character count per text from 70 to 160.
How do you identify unicode characters?
Copy and paste your message into the message window above. GSM characters will be displayed in different colours depending on which character set the characters belong to:
The unicode character finder will then identify any unicode characters which you can then make changes and check again.
SMS Character Counter
The tool also includes an sms character counter so you can check your text messages contain the expected number of characters and will use the expected number of SMS credits.
A standard text contains 160 characters including spaces. Any message over 160 characters will be sent a multipart message. Longer messages are charged at 153 characters per text; the remaining 7 characters are used to ensure that they are re-combined into a single message when they reach the handset.
The maximum message length is 1280 characters and will use 8 credits.
Reasons to use the Unicode Character identifier
There are important reasons to make the unicode identifier a part of your workflow:
- Identify and eliminate unicode characters in your texts, avoiding costly SMS credits overuse
- Identify the precise number of characters that are being used to send a message
- Calculate the number of message credits used to send your messages
Which characters commonly cause a message to be sent in unicode?
Sometimes a message may appear to contain no unicode characters, yet the message is still being sent as unicode.
There are a couple of likely culprits, which are most commonly copied and pasted from word processing packages such as Microsoft Word.
These are the comma, the apostrophe and, to a lesser extent, double quote marks.
GSM commas and apostrophes are simple vertical lines, whereas Word's versions are rich text characters and curve to the left.
